Introduction
MQTT over QUIC, introduced by the world’s leading open-source distributed MQTT broker, EMQX 5.0, combines the advantages of the MQTT protocol with the characteristics of QUIC. By leveraging QUIC's low connection overhead and multi-path support, MQTT over QUIC offers a promising solution to improve user experience in weak networks and irregular network paths. It can address connection interruptions and slow establishment in IoT scenarios such as connected vehicles operating in challenging environments like mountainous areas or tunnels.
With the continuous development of cloud native, more and more users deploy EMQX clusters on Kubernetes to enjoy the rapid creation and convenient management. This article will introduce how to deploy EMQX clusters on Kubernetes and enable MQTT over QUIC.
Expose EMQX Service
When deploying EMQX on Kubernetes, you can use LoadBalancer or NodePort to expose EMQX service to clients outside the cluster.
The
LoadBalancermethod relies on the cloud vendor's load balancer to provide services. Currently, the cloud vendor's load balancer does not support the address migration feature of QUIC.The
NodePortmethod relies on kube-proxy component of Kubernetes to forward external requests, which can seamlessly connect to EMQX services and supports the QUIC address migration feature.
In the scenario of the Internet of Vehicles, the address of the vehicle end may change frequently, and the address migration feature of QUIC is particularly important. Therefore, when deploying EMQX 5.0 on Kubernetes with MQTT over QUIC, we'd better choose to expose services outside the cluster in the form of NodePort.
Next, we will introduce the detailed process of deploying EMQX 5.0 on Kubernetes with MQTT over QUIC . At the same time, we will provide a test sample of exposing services in the form of NodePort and QUIC address migration verification.
Prerequisites
Before deploying EMQX 5.0 on Kubernetes, make sure the following requirements are satisfied:
Kubernetes: version >= 1.24
Due to the bug of IPVS break UDP NodePort Services when kube-proxy in ipvs mode processes UDP packets, UDP packets are discarded, so When deploying Kubernetes, we recommend using kube-proxy in iptables mode. This bug has been fixed in K8s 1.27, please refer to: Syncing IPVS conntrack cleaning with IPTables.
Helm: version >= 3
Install EMQX Operator
Install and start
cert-manager.cert-managerversion1.1.6or higher is required. Skip this step if thecert-manageris already installed and started.$ helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io $ helm repo update $ helm upgrade --install cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager \ --namespace cert-manager \ --create-namespace \ --set installCRDs=trueOr you can follow the cert-manager installation guide to install it.
Install EMQX Operator by Helm.
$ helm repo add emqx https://repos.emqx.io/charts $ helm repo update $ helm install emqx-operator emqx/ emqx-operator --namespace emqx-operator-system --create-namespaceWait till EMQX Operator is ready.
$ kubectl wait --for=condition=Ready pods -l "control-plane=controller-manager" -n emqx-operator-system # If you get output results similar to the following, it indicates that emqx-operator is ready: pod/emqx-operator-controller-manager-57bd7b8bd4-h2mcr condition met
Deploy EMQX 5.0 With MQTT over QUIC
Save the following as a YAML file and deploy it with the
kubectl applycommand.apiVersion: apps.emqx.io/v2alpha1 kind: EMQX metadata: name: emqx spec: image: emqx:5.0 bootstrapConfig: | listeners.quic.default { enabled = true bind = "0.0.0.0:14567" max_connections = 1024000 keyfile = "/opt/emqx/etc/certs/key.pem" certfile = "/opt/emqx/etc/certs/cert.pem" } coreTemplate: spec: replicas: 3 replicantTemplate: spec: replicas: 3 listenersServiceTemplate: spec: type: NodePort ports: - name: quic-default protocol: UDP port: 14567 targetPort: 14567listeners.quic.defaultmeans to enable the QUIC listener and bind the UDP14567port.Wait till EMQX cluster is ready. You can check the status of EMQX cluster through the
kubectl getcommand and please make sure thatSTATUSisRunning. This may take some time.$ kubectl get emqx NAME IMAGE STATUS AGE emqx emqx:5.0 Running 10mObtain Listener Service of EMQX Cluster.
EMQX Operator will create two EMQX Service resources, one is
emqx-dashboardand the other isemqx-listeners, corresponding to EMQX console and EMQX listening port respectively.$ kubectl get service emqx-listeners NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE emqx-listeners NodePort 192.168.50.64 <none> 14567:30171/UDP,1883:32633/TCP 2m1s
You can see that the QUIC listener is enabled in the service.
Test QUIC With eMQTT-Bench
eMQTT-Bench is a lightweight MQTT 5.0 benchmark tool written in Erlang. You can download and install eMQTT-Bench that supports the QUIC protocol for your platform from eMQTT-Bench release.
Use QUIC protocol to initiate a connection and subscribe by specifying
--quicoption. Here 10 clients are used to subscribe tot/testtopic.$ ./emqtt_bench sub --quic -h ${node_ip} -p ${node_port} -t t/test -c 10Open another terminal, and use QUIC protocol to connect and perform a release test.
$ ./emqtt_bench pub --quic -h ${node_ip} -p ${node_port} -t t/test -c 1At this point, you can see the message subscription publishing rate of the subscriber and publisher from the output log of the command line:
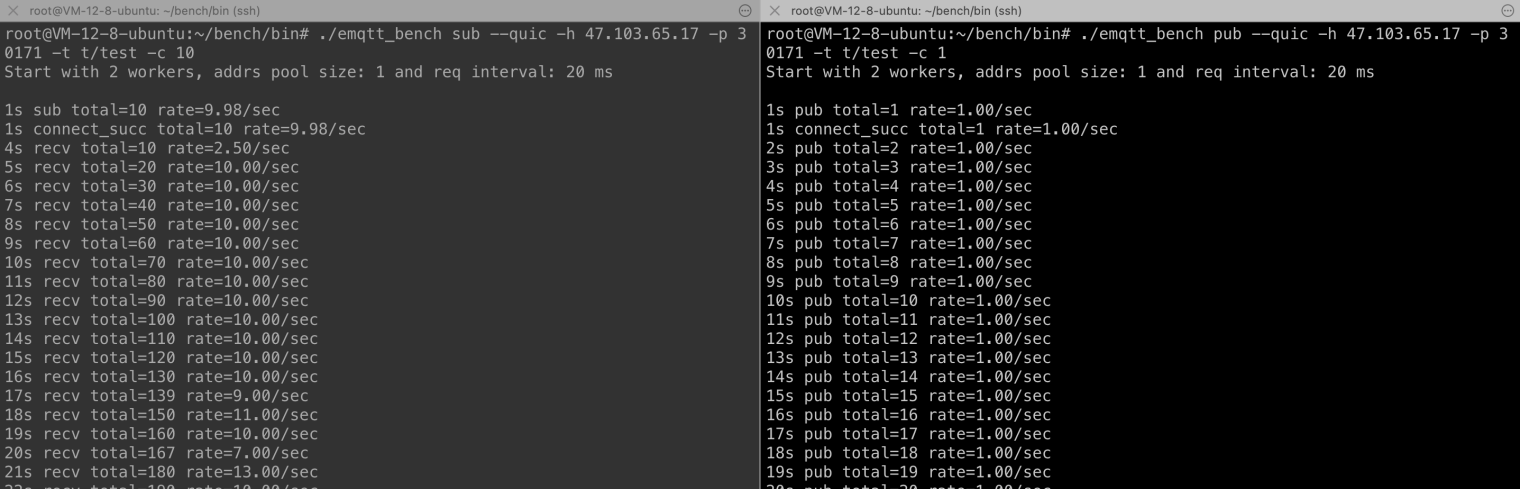
Test address migration.
We switch the client network from the time point indicated by the arrow in the figure, and observe the sending and receiving of EMQX cluster messages as shown in the figure below:
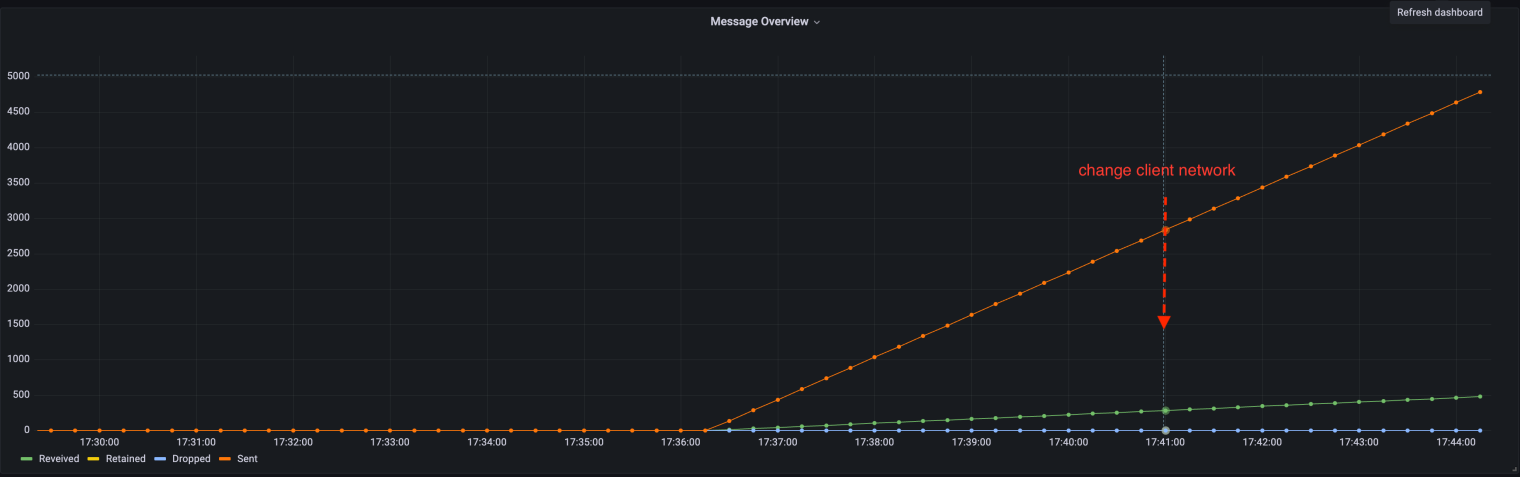
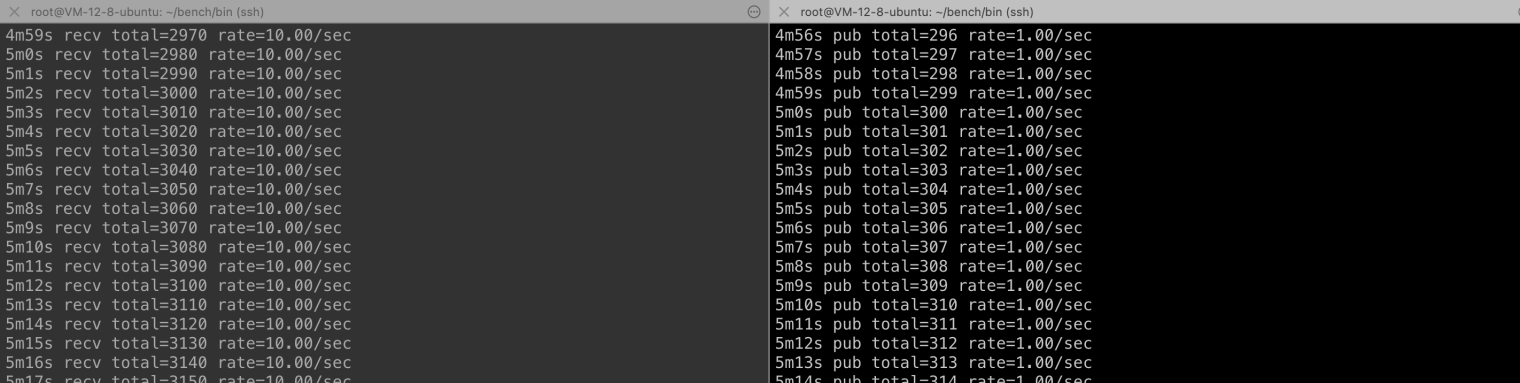
It can be seen from the above figure that QUIC has no effect on message receiving and sending when the client network changes. At the same time, the client publishes and subscribes to messages without any impact, as shown in the following figure:
Challenges in Using QUIC on Kubernetes
There are currently two major problems in using the QUIC protocol on Kubernetes:
The cloud vendor LoadBalancer has limited support for the QUIC protocol, such as not supporting IETF QUIC protocol and QUIC address migration feature.
When using
NodePortto expose QUIC services outside the cluster, if kube-proxy adopts the ipvs mode, it will trigger the bug of kube-proxy, causing UDP packets to be discarded, thus causing the EMQX QUIC service to be unavailable.
Conclusion
The above is the initial experience of MQTT over QUIC on Kubernetes with EMQX 5.0. It can be seen that deploying EMQX 5.0 on Kubernetes is very simple, with only one YAML file needed. After enabling MQTT over QUIC, your device can communicate with the EMQX cluster based on QUIC protocol and take advantage of its benefits for IoT messaging.
