Table of Contents
Introduction
A rule engine is a software system that utilizes predefined rules to make decisions or take actions based on input data. In this blog post, we will introduce the Rule Engine in EMQX MQTT Broker and explains why it is essential for MQTT message transformation and data integration. We will also provide a quick guide with examples to help you get started with Rule Engine for MQTT.
What is Rule Engine for MQTT?
MQTT is an efficient and reliable messaging protocol for low-bandwidth, high-latency networks, which is common in IoT scenarios. In the context of MQTT's publish/subscribe model, an MQTT broker receives messages from publishers and routes them to subscribers, ensuring that messages are delivered reliably and efficiently.
Rule Engine for MQTT is a software component that allows users to define and execute rules based on MQTT messages. The Rule Engine can be used to extract, filter, enrich, and transform MQTT messages, as well as trigger actions based on specific criteria. This helps to reduce manual intervention and accelerate data integration and application development.
Use Cases of Rule Engine in MQTT Broker
The rule engine has a wide range of applications in MQTT brokers and can be used to automate tasks, monitor systems, and improve overall efficiency and safety. Let’s take some examples:
In smart home automation, the rule engine can be used to automate tasks such as turning on lights when someone enters a room or adjusting the thermostat based on the time of day. This can improve energy efficiency and make daily life more convenient for homeowners.
In industrial IoT applications, it can be used to monitor and control complex systems, such as manufacturing processes or power grids. The rule engine can help prevent equipment failures and improve overall system performance by setting up rules to detect and respond to anomalies.
In the healthcare industry, it can be used to monitor patient health and alert medical professionals to potential issues.
EMQX’s Built-in, Out-of-Box Rule Engine
EMQX is an open-source, highly scalable MQTT broker integrated with an embedded rule engine component. It allows users to quickly implement business logic on data processing with low code, simplifying their software architecture's complexity.
There are two reasons for embedding a rule engine feature instead of relying on a separate rule engine outside of the broker:
First, embedding the broker rule engine enables more efficient and streamlined communication. The rule engine can access MQTT messages directly, eliminating the need for extra communication channels or protocols, which reduces latency and enhances system performance.
Second, this allows for easier deployment and management of the overall system. By deploying the rule engine and the broker together as a single component, it eliminates the need to integrate and manage them separately, resulting in a simplified deployment process and a less complex system.
Rule Engine Quick Start
We'll provide a quick guide to the rule engine using EMQX Enterprise as an example to take advantage of its rich data integration actions and resources.
Download EMQX Enterprise.
Choose the latest version of EMQX Enterprise 4.4 in the drop-down list:
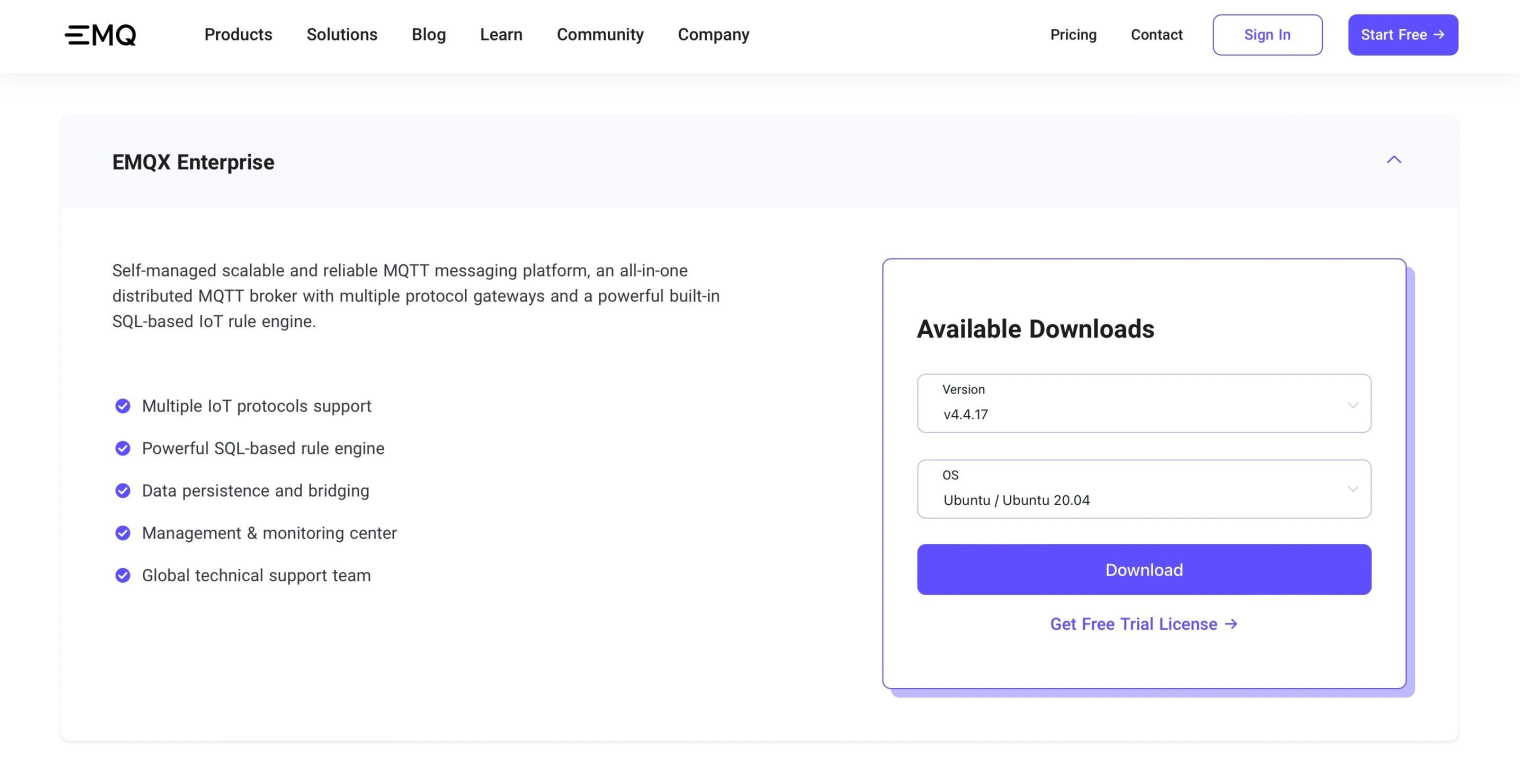
The default license of EMQX Enterprise allows up to 10 MQTT connections, which should be enough for us to experience the functionality of the rule engine. If you want to establish more MQTT connections, click the link below "Download" to obtain a valid license for 15 days.
Here we take Ubuntu 20.04 as an example to download the EMQX Enterprise version 4.4.17 package:
$ wget https://www.emqx.com/en/downloads/enterprise/4.4.17/emqx-ee-4.4.17-otp24.3.4.2-1-ubuntu20.04-amd64.zip
$ unzip emqx-ee-4.4.17-otp24.3.4.2-1-ubuntu20.04-amd64.zip
Now it's time to start the EMQX broker:
$ cd emqx
$ ./bin/emqx start
Alternatively, Try Our Hosted MQTT Broker on EMQX Cloud
Suppose you don't want to bother installing a Linux operating system, downloading and installing EMQX, or executing those Linux commands. In that case, you can use EMQX Cloud to experience the rule engine feature. What you need is to do some simple configuration on the web page.
Configure a Simple Rule that Republish MQTT Messages to Another Topic
The Requirement
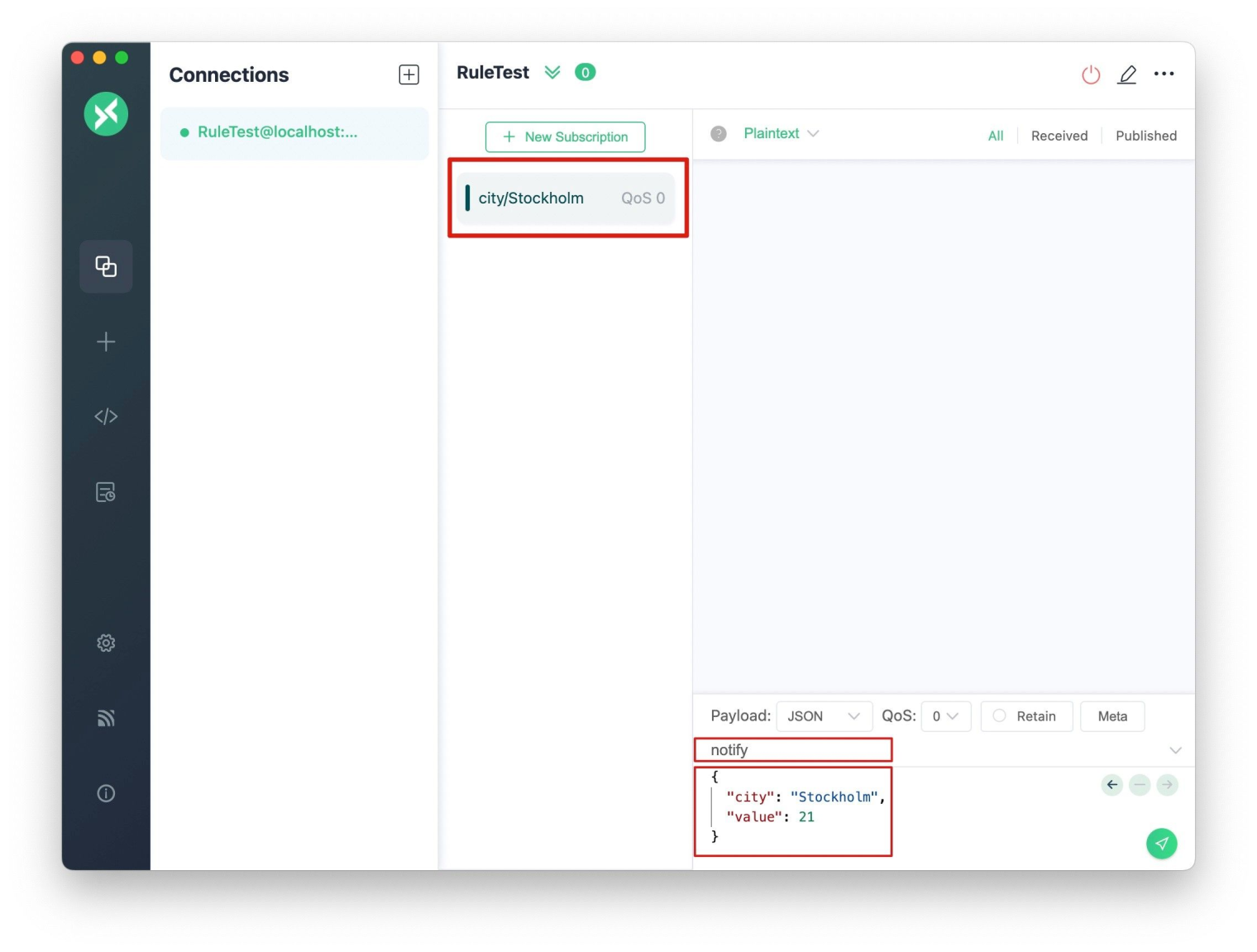
For example, we assume a device with the username of "Steve” periodically sends messages to the notify topic in JSON format. Below is an example of the message sent by the device:
{"city": "Stockholm", "value": 21}
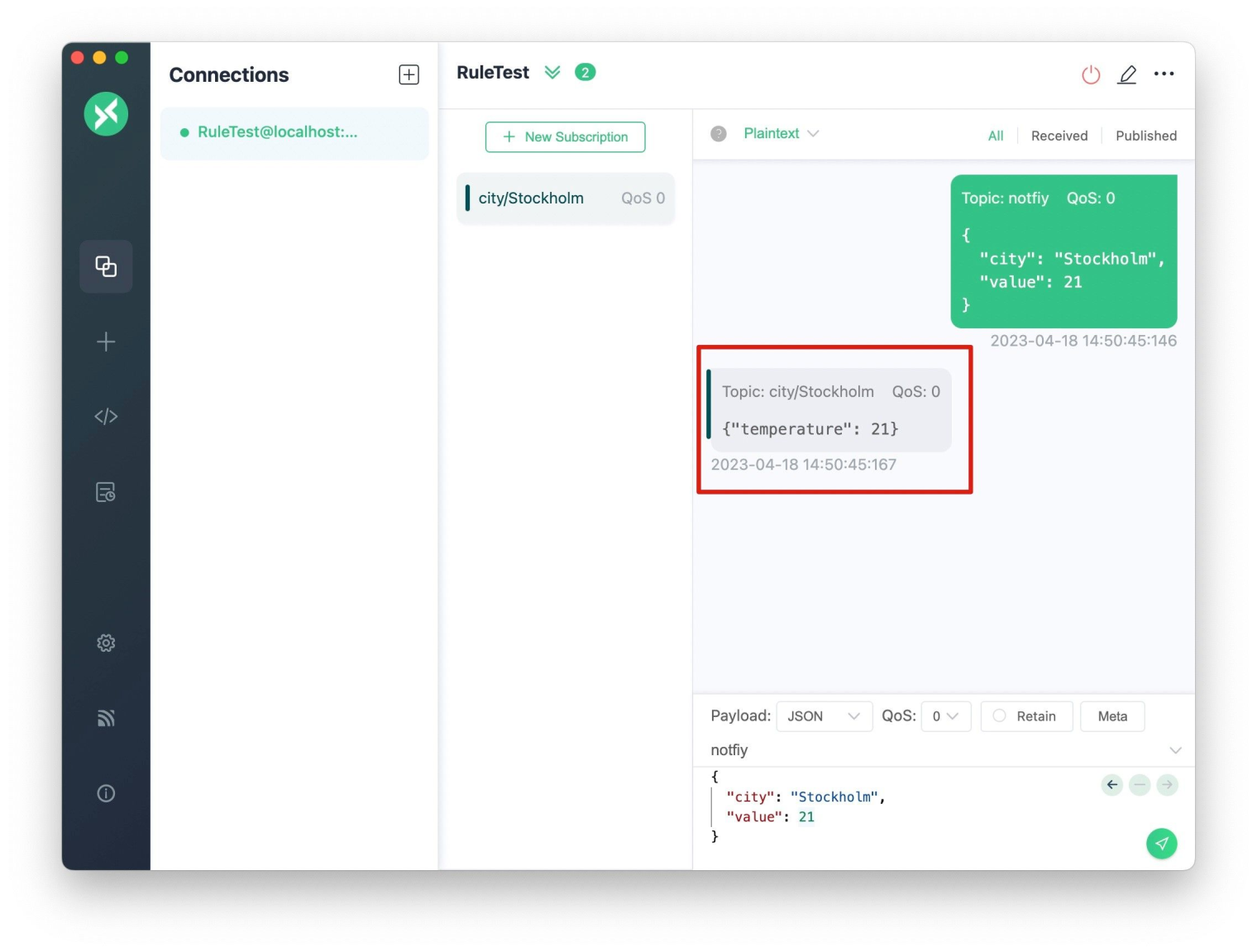
We want to send new messages to a dynamic MQTT topic, city/Stockholm, based on the value of the city field in the original message. Additionally, we want to extract the value of the value field from the original message and use it to construct a new message with a temperature field:
{"temperature": 21}
Design the SQL of the Rule
Now that we have understood the requirements let's open the EMQX Dashboard (http://localhost:18083) to create a rule (the default username/password of the dashboard is admin/public).
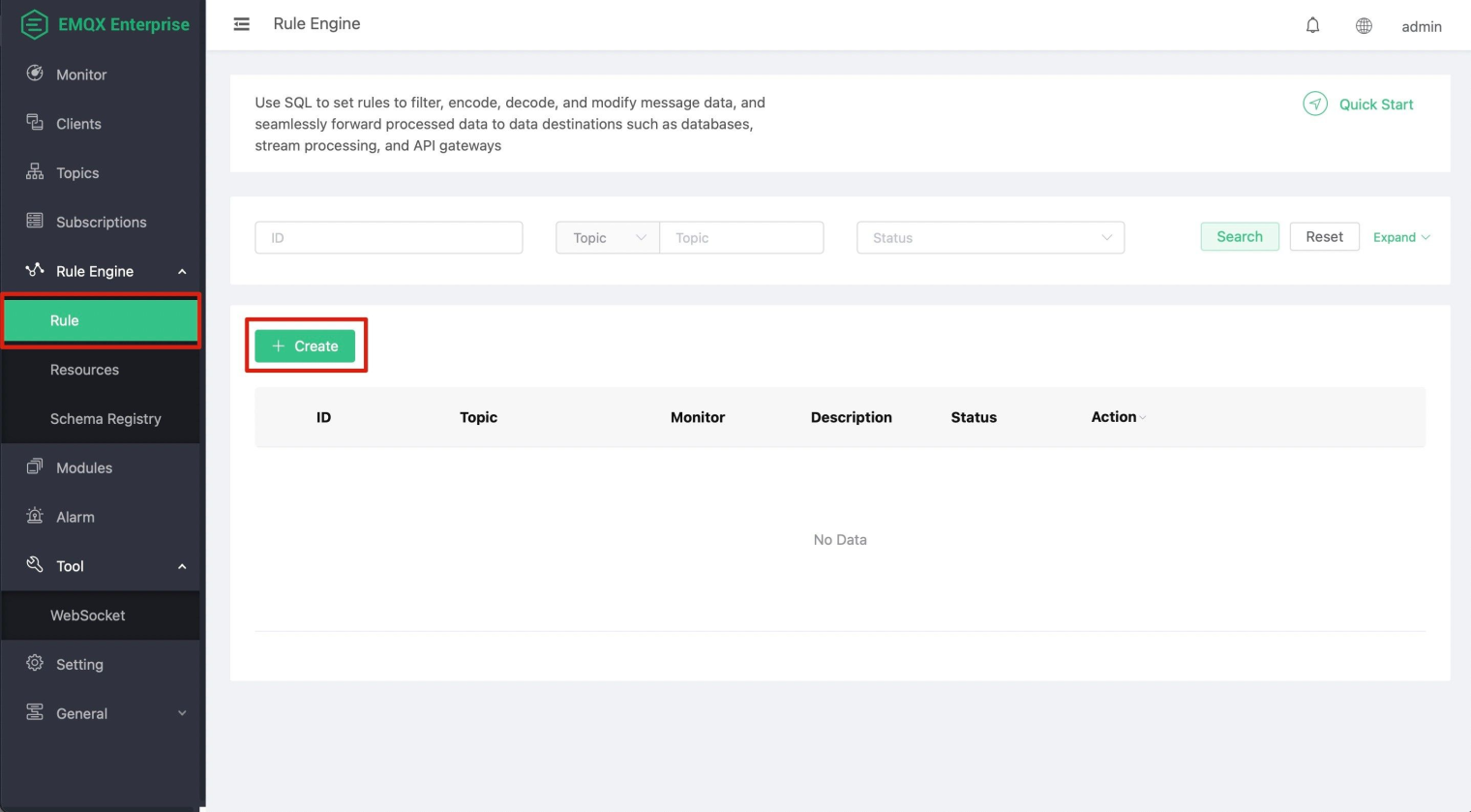
To meet the aforementioned requirements, we need the following SQL statement:
SELECT
payload.city as city,
payload.value as val
FROM
"notify"
WHERE
username = 'Steve'
We are only interested in messages with the topic notify, so we specified it in the FROM clause. And the WHERE clause is used to filter messages with the username field equal to Steve.
The SELECT statement assigns the values of the city and value fields in the original message to two new variables: city and val. We will use them when we create the action later.
Bind a Republish Action to the Rule
Then we need to bind a Republish action and fill in the parameters of the action:
Target Topic:
city/${city}Payload Template:
{"temperature": ${val}}
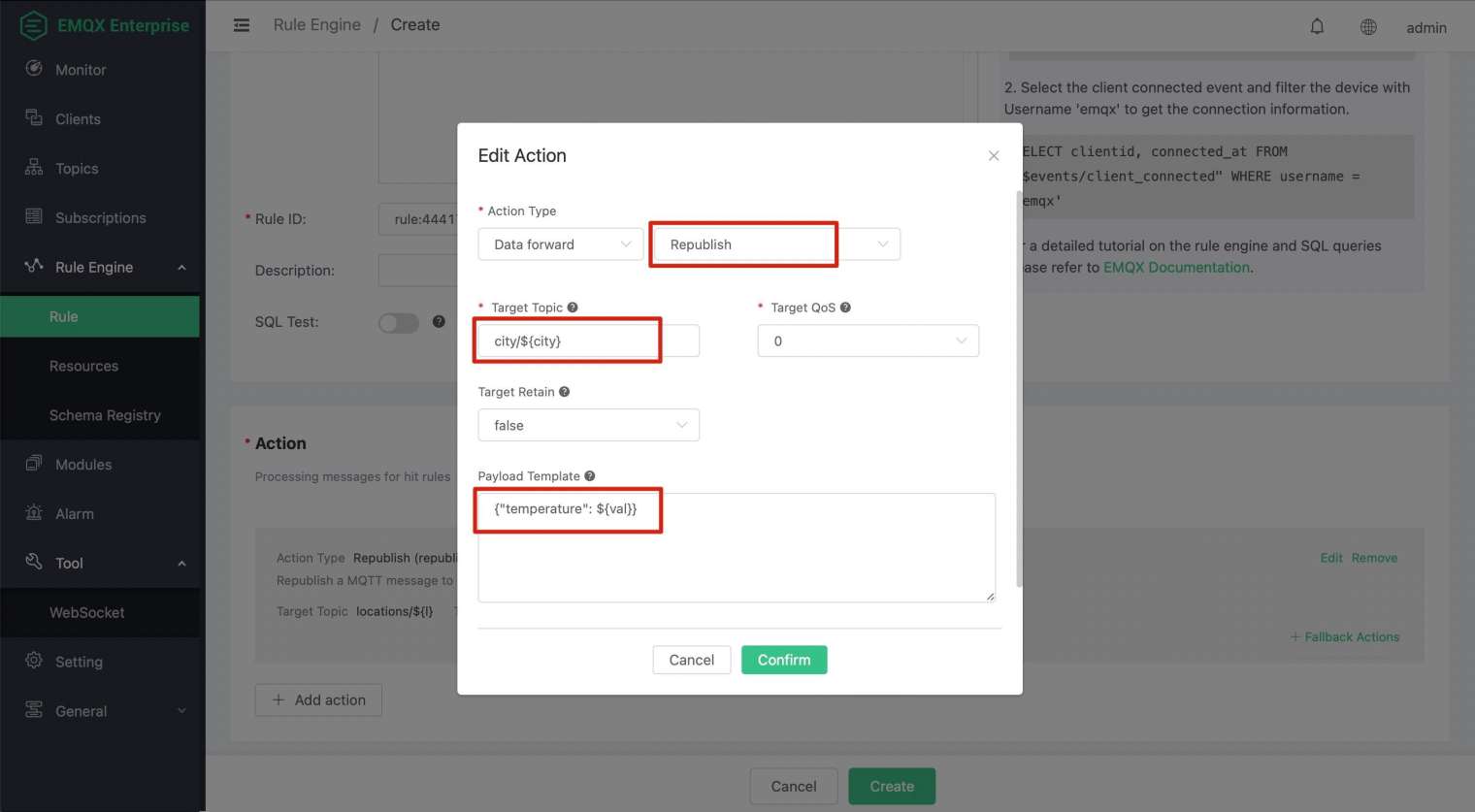
Recall that the SELECT statement in the previous section assigns the values of the payload.city and payload.value to two new variables: city and val. Our Republish action references these variables using ${city} and ${val} placeholders, and the rule engine will replace the values of the variables at runtime in the corresponding positions.
Test the Rule
With the rule and action created, we can now test the rule by publishing a message to the broker that matches the conditions.
We will use an MQTT client tool called MQTTX for the testing. You can download and install it from here.
First, we create an MQTT connection, setting the username to "Steve".
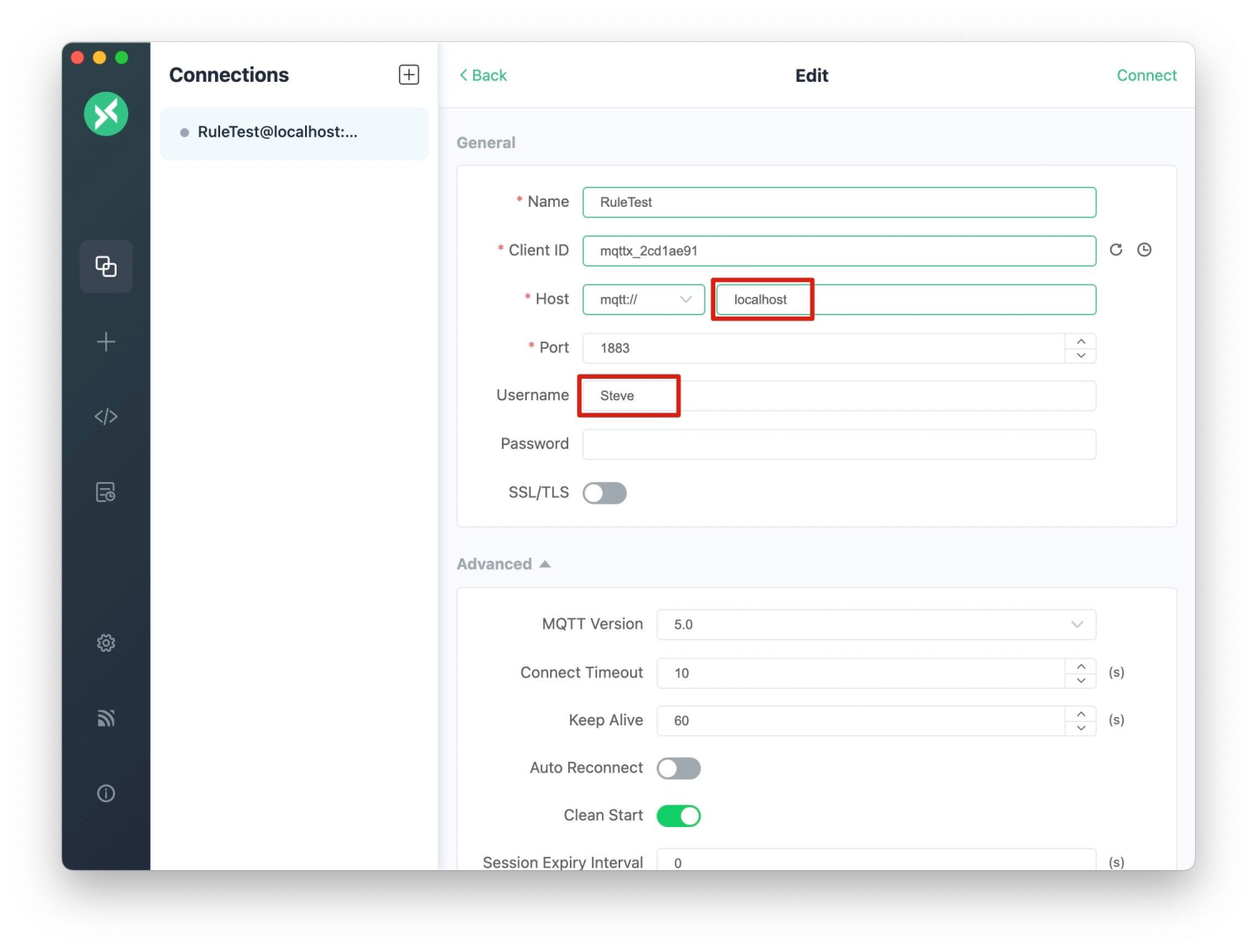
Then, we subscribe to the target topic city/Stockholm, and publish a message to the notify topic:
We did it! We have received the message forwarded by the rule:
Conclusion
Rule Engine for MQTT is a powerful tool for automating actions based on specific conditions or events in IoT applications. With the quick start guide and examples in this article, you can quickly get started with Rule Engine in EMQX and take advantage of it in your IoT projects.
The rule engine in EMQX Enterprise also includes rich data integration actions and resources, which can quickly and efficiently implement most business logic related to data processing. We highly recommend you to explore and experience it yourself freely. For more detailed documentation on the rule engine SQL syntax, please refer to the Docs for Rule SQL.
