Introduction
As IoT technology advances rapidly, it becomes easier to interact with devices and among devices. However, the new challenge in the IoT field is making the interaction more natural, efficient, and smart.
Advanced Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT, GPT-3.5, and GPT-4, created by OpenAI, have gained much popularity around the world lately. This has created many opportunities for combining General Artificial Intelligence (AGI) with the IoT domain, offering promising avenues for future progress.
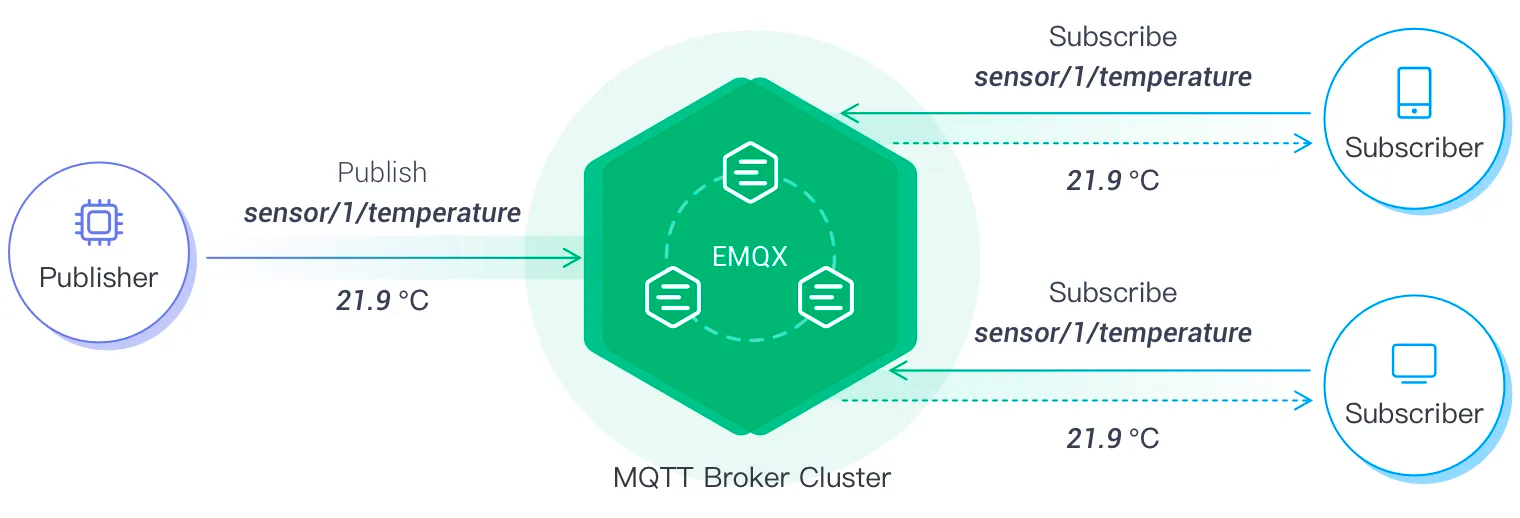
ChatGPT is an advanced natural language processing application that can easily achieve natural conversations with humans with its excellent natural language processing skills. Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) is the main protocol in IoT that enables real-time and efficient data transmission through lightweight and low bandwidth communication and publish/subscribe model.
By combining the MQTT protocol with ChatGPT, we can envision a future where intelligent human-machine interaction in the IoT field becomes more seamless and accessible.
ChatGPT enables users to control their smart home devices using natural dialogue in the smart home field, enhancing their overall living experience.
In the field of industrial automation, ChatGPT aids engineers in efficiently analyzing equipment data, leading to increased productivity and effectiveness.
…
This blog will show you how to combine the MQTT protocol with a natural language processing application like ChatGPT and give you a simple example of using them together for intelligent applications in the IoT field.
Basic Concepts
Before we start, let's have a quick overview of some fundamental concepts of MQTT and ChatGPT.
MQTT
As mentioned earlier, the MQTT protocol is a lightweight messaging protocol that uses publish/subscribe model. It is widely applied in various fields such as IoT, mobile Internet, smart hardware, Telematics, smart city, telemedicine, power, oil, and energy.
To learn more about MQTT please refer to MQTT Protocol Explained: The Basics and a Quick Tutorial
The MQTT broker is the key component for connecting many IoT devices using the MQTT protocol. We will use EMQX, a highly scalable MQTT broker, in our solution to ensure efficient and reliable connection of massive IoT devices and real-time handling and delivery of message and event stream data.
The world's most scalable MQTT Broker for IoT
For more information please refer to EMQX
We can use an MQTT client to connect to the MQTT broker and communicate with IoT devices. In this blog, we use MQTTX, a cross-platform open-source MQTT client that provides desktop, command line, and web-based applications. It can test the connection with MQTT brokers and help developers quickly develop and debug MQTT services and applications.
ChatGPT
GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) is a deep learning model that excels at text generation and understanding. ChatGPT can comprehend and produce natural language and have natural and smooth dialogues with users. We need to use the API that OpenAI offers to communicate with the GPT model to achieve ChatGPT's natural language processing skills.
ChatGPT Interface
Solution Design and Preparation
Utilizing the functionalities of the MQTT protocol and ChatGPT, we aim to devise a solution enabling seamless integration and interoperability between the two.
We will use the API that OpenAI offers to communicate with the GPT model and write a client script to achieve ChatGPT-like natural language processing functionality. The MQTT client in this script will receive the message and send it to the API, generating the natural language response. The response will be published to a specific MQTT topic to enable the interaction cycle between ChatGPT and MQTT client.
We will show the interaction process between ChatGPT and MQTT protocol for message receiving, handling, and delivery through this solution.
Please follow the steps below to get ready with the necessary tools and resources.
Install EMQX:
You can use Docker to install and launch EMQX 5.0 quickly:
docker run -d --name emqx -p 1883:1883 -p 8083:8083 -p 8883:8883 -p 8084:8084 -p 18083:18083 emqx/emqx:latestYou can also install EMQX using RPM or DEB packages besides Docker. Please see EMQX 5.0 Installation Guide for more details.
Install the MQTTX desktop application:
Go to the MQTTX website and choose the version that matches your OS and CPU architecture. Then, download and install it.
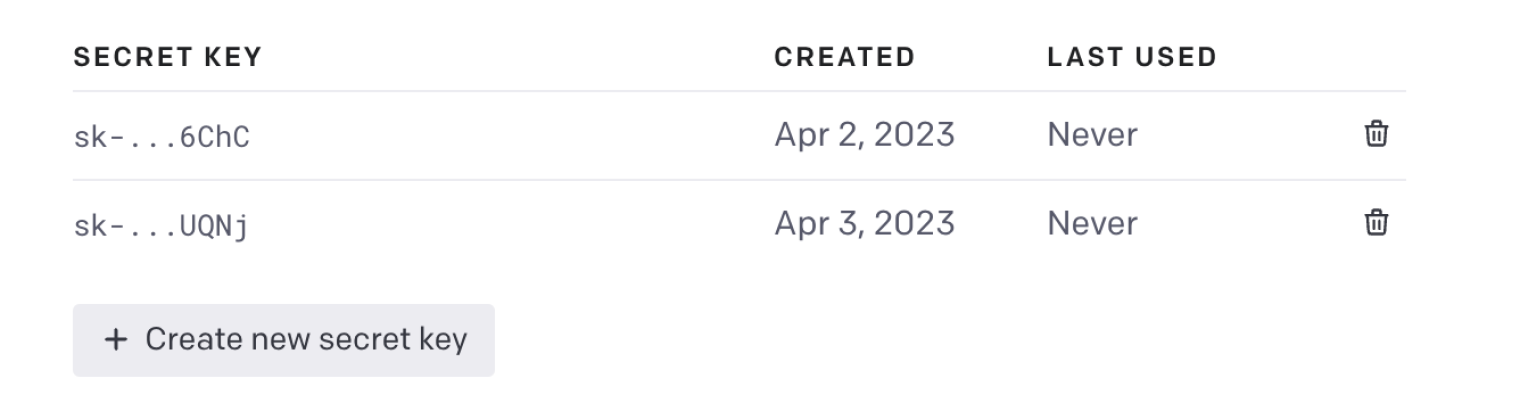
Sign up for an OpenAI account and get an API key:
Go to OpenAI and sign in or create an account. After that, click on the top right corner and choose
View API Keys. Then, under theAPI keyssection, clickCreate new secret keyto make a new API key. Please store this key securely as you will need it for API authentication in later programs.
Once you finish these steps, you will have the tools and resources to integrate the MQTT protocol with ChatGPT. For more information and learning materials on how to work with the GPT language model using OpenAI's API, you can check out the OpenAI documentation.
Coding
After setting up the resources and environment, we will build an MQTT client using the Node.js environment. This client will get messages from an MQTT topic, send data to the OpenAI API, and create a natural language with the GPT model. The natural language created is then published to the specific MQTT topic for integrated interaction. You can also use other programming languages like Python, Golang, etc. based on your needs and familiarity. We will use the API directly to provide a user-friendly illustration, but you can also use the official library, which offers a simpler way to use Node.js and Python.
For more information please refer to OpenAI Libraries.
Set up the Node.js environment. Make sure Node.js is installed (v14.0 or higher is recommended). Make a new project folder and initialize the project with the npm init command. Then, use this command to install the required dependency packages:
npm init -y npm install axios mqtt dotenvWe use axios to send HTTP requests, mqtt to connect to MQTT servers, and dotenv to load environment variables.
Use environment variables. Create a file named
.envand put your OpenAI API key in it:OPENAI_API_KEY=your_openai_api_keyCode the program. Create a new
index.jsfile where you connect to the MQTT broker, subscribe to the specific MQTT topic, and listen for messages. When a message is received, use axios to send an HTTP request to the OpenAI API, create a natural language response, and publish the response to the specific MQTT topic. The following is a list of key codes for each step for your reference:Use the MQTT library to connect to the MQTT broker and subscribe to the
chatgpt/request/+topic by default to get incoming MQTT messages:const host = "127.0.0.1"; const port = "1883"; const clientId = `mqtt_${Math.random().toString(16).slice(3)}`; const OPTIONS = { clientId, clean: true, connectTimeout: 4000, username: "emqx", password: "public", reconnectPeriod: 1000, }; const connectUrl = `mqtt://${host}:${port}`; const chatGPTReqTopic = "chatgpt/request/+"; const client = mqtt.connect(connectUrl, OPTIONS);Create a
genTextfunction that runs asynchronously and takes the userId parameter. Use axios to make an HTTP client instance and authenticate with the OpenAI API key in the HTTP Headers. Then, make a POST request to the OpenAI API to generate natural language replies. Use the MQTT client to publish the generated replies to a specific topic to which the user is subscribed. Store the historical messages in the Messages array.// Add your OpenAI API key to your environment variables in .env const OPENAI_API_KEY = process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY; let messages = []; // Store conversation history const maxMessageCount = 10; const http = axios.create({ baseURL: "https://api.openai.com/v1/chat", headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json", Authorization: `Bearer ${OPENAI_API_KEY}`, }, }); const genText = async (userId) => { try { const { data } = await http.post("/completions", { model: "gpt-3.5-turbo", messages: messages[userId], temperature: 0.7, }); if (data.choices && data.choices.length > 0) { const { content } = data.choices[0].message; messages[userId].push({ role: "assistant", content: content }); if (messages[userId].length > maxMessageCount) { messages[userId].shift(); // Remove the oldest message } const replyTopic = `chatgpt/response/${userId}`; client.publish(replyTopic, content, { qos: 0, retain: false }, (error) => { if (error) { console.error(error); } }); } } catch (e) { console.log(e); } };Finally, save received messages with the topic
chatgpt/request/+in the Messages array and call thegenTextfunction to generate and send natural language replies directly to the specific topic to which the user is subscribed. The Messages array can hold up to 10 historical messages.client.on("message", (topic, payload) => { // Check if the topic is not the one you're publishing to if (topic.startsWith(chatGPTReqTopicPrefix)) { const userId = topic.replace(chatGPTReqTopicPrefix, ""); messages[userId] = messages[userId] || []; messages[userId].push({ role: "user", content: payload.toString() }); if (messages[userId].length > maxMessageCount) { messages[userId].shift(); // Remove the oldest message } genText(userId); } });
Run the script:
node index.js
We have now finished the fundamental functional aspect of the demo project. Apart from providing the core functionality, the code incorporates a feature that allows users to have access isolation by appending distinct suffixes to specific topics. By preserving the history of previous messages, the GPT model can grasp the context of the conversation and generate responses that are more coherent and contextual, using information from past interactions.
The full code is available on GitHub at openai-mqtt-nodejs.
Alternative Solution
Apart from the above example, another approach to speed up development is to use the EMQX's rule engine and Webhook from the data bridging function.
EMQX enables the configuration of rules that initiate a Webhook callback when sending a message to a specific topic. We need to code a simple web service that uses the OpenAI API to work with the GPT model and return the replies created by the GPT model via HTTP. To accomplish the goal of integrated interaction, we have two options: either create a new MQTT client to publish the GPT model's replies to a specific topic, or directly employ the EMQX Publish API. Both approaches allow us to achieve the desired outcome of seamless interaction.
This approach can save development costs and quickly build PoC or Demo for users with web services. It does not require an independent MQTT client and uses the EMQX rule engine to simplify the integration process and flexibly handle data. However, it still requires developing and maintaining web services, and Webhook may not be easy and convenient for complex application scenarios.
Each of the solutions mentioned above has its benefits, and we can pick a more appropriate solution based on actual business requirements and developer skill level. In any case, EMQX, as the MQTT infrastructure, provides important support for system integration, enabling developers to create project prototypes and advance digital transformation quickly.
Demo
We can use the MQTTX desktop client to test this demo project after developing the interaction between the MQTT client and the GPT model. The user interface of MQTTX is similar to chat software, making it easier and more suitable for showing interaction with chatbots.
First, we need to create a new connection in MQTTX that connects to the same MQTT server as the one used in the previous code examples, that is, 127.0.0.1 . Then, subscribe to the chatgpt/response/demo topic to receive replies and send messages to the chatgpt/request/demo topic. The demo suffix here can be changed to other strings to isolate access between users. We can test this by sending a Hello message:
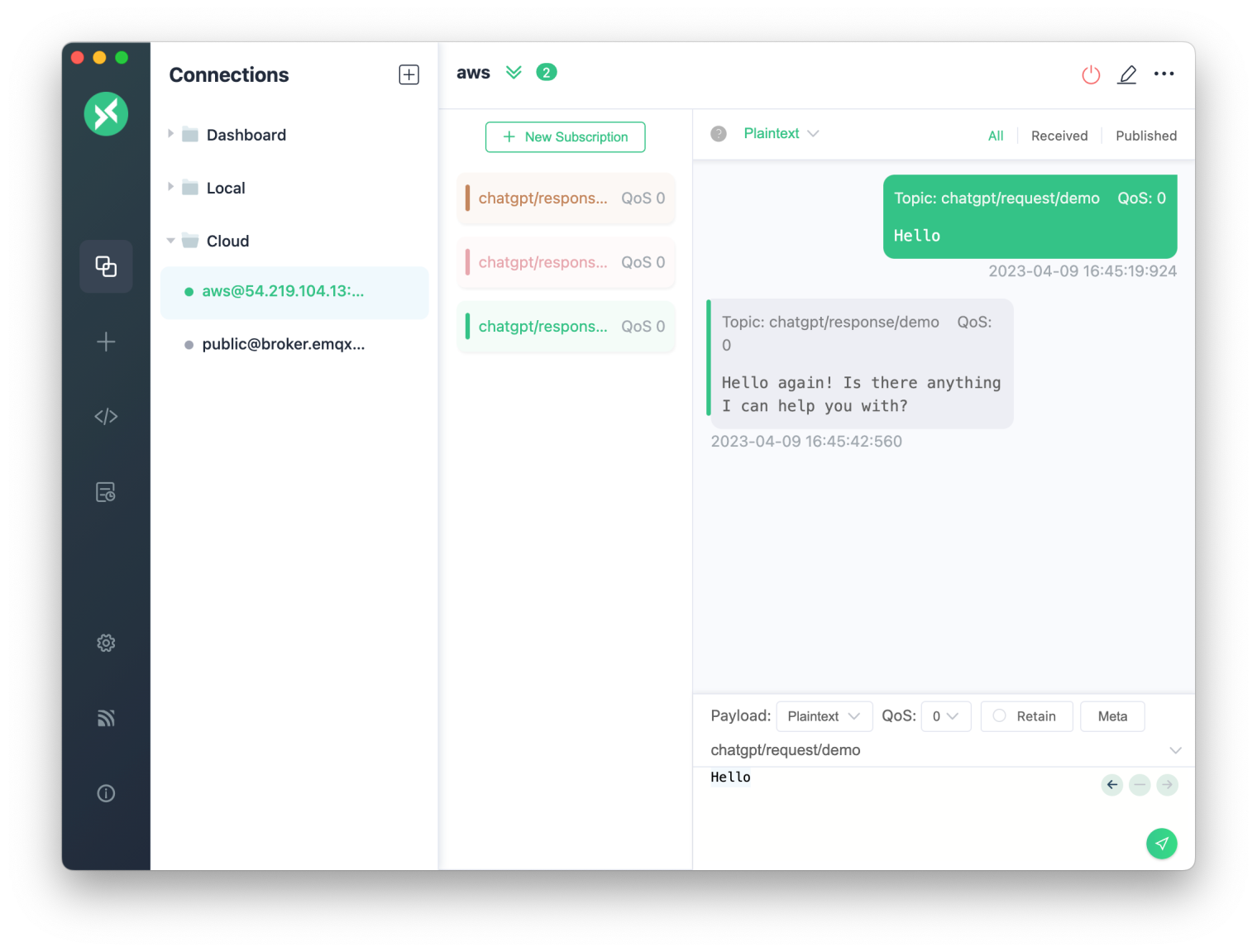
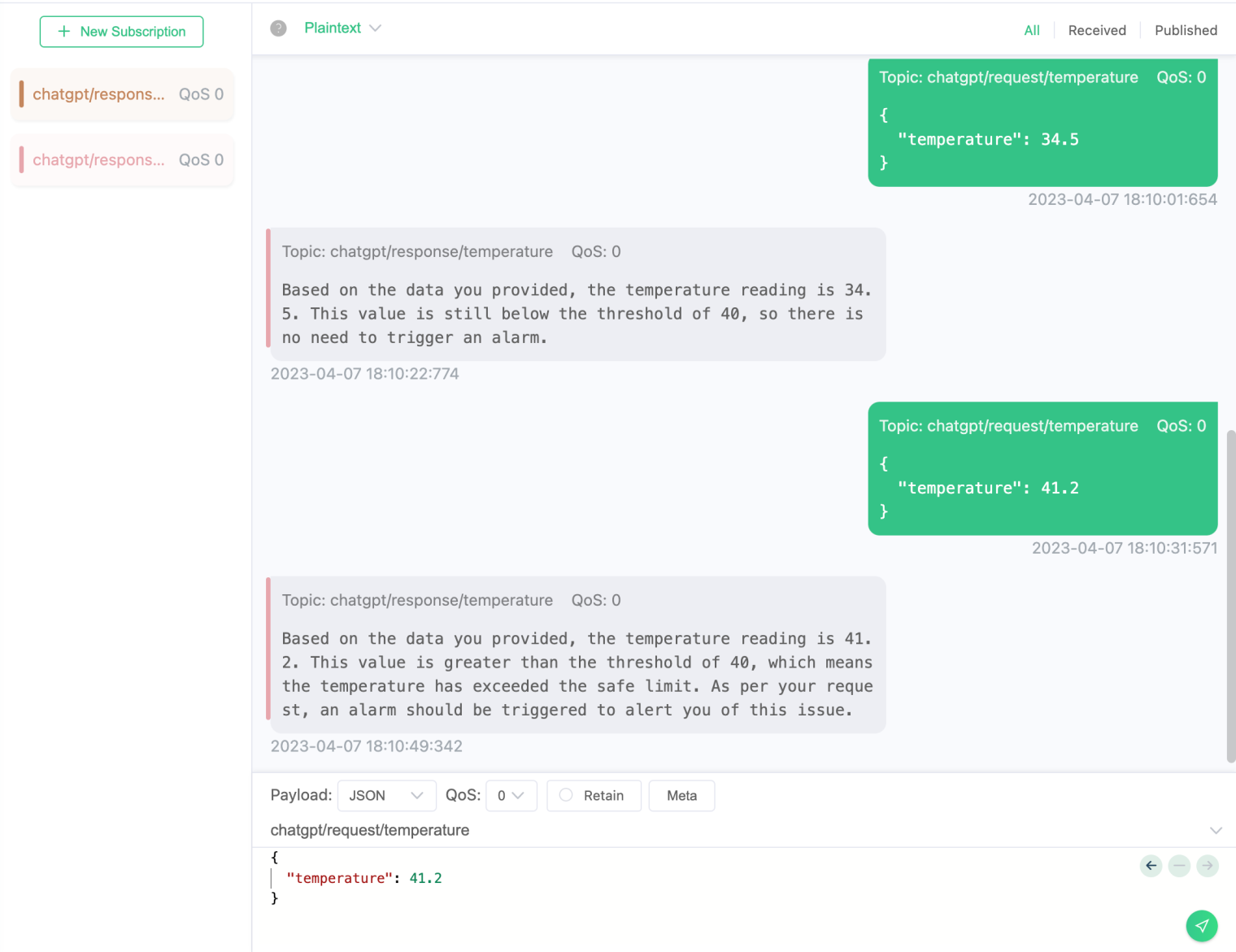
Next, we create some more complex demo environments. When the temperature of a sensor goes beyond a preset threshold, the ChatGPT robot will send an alert message to another MQTT topic, which is connected to a monitoring device, such as a smart watch or smart speaker. The monitoring device can use natural language technology to turn the alert information into speech so that users can receive and understand it more easily.
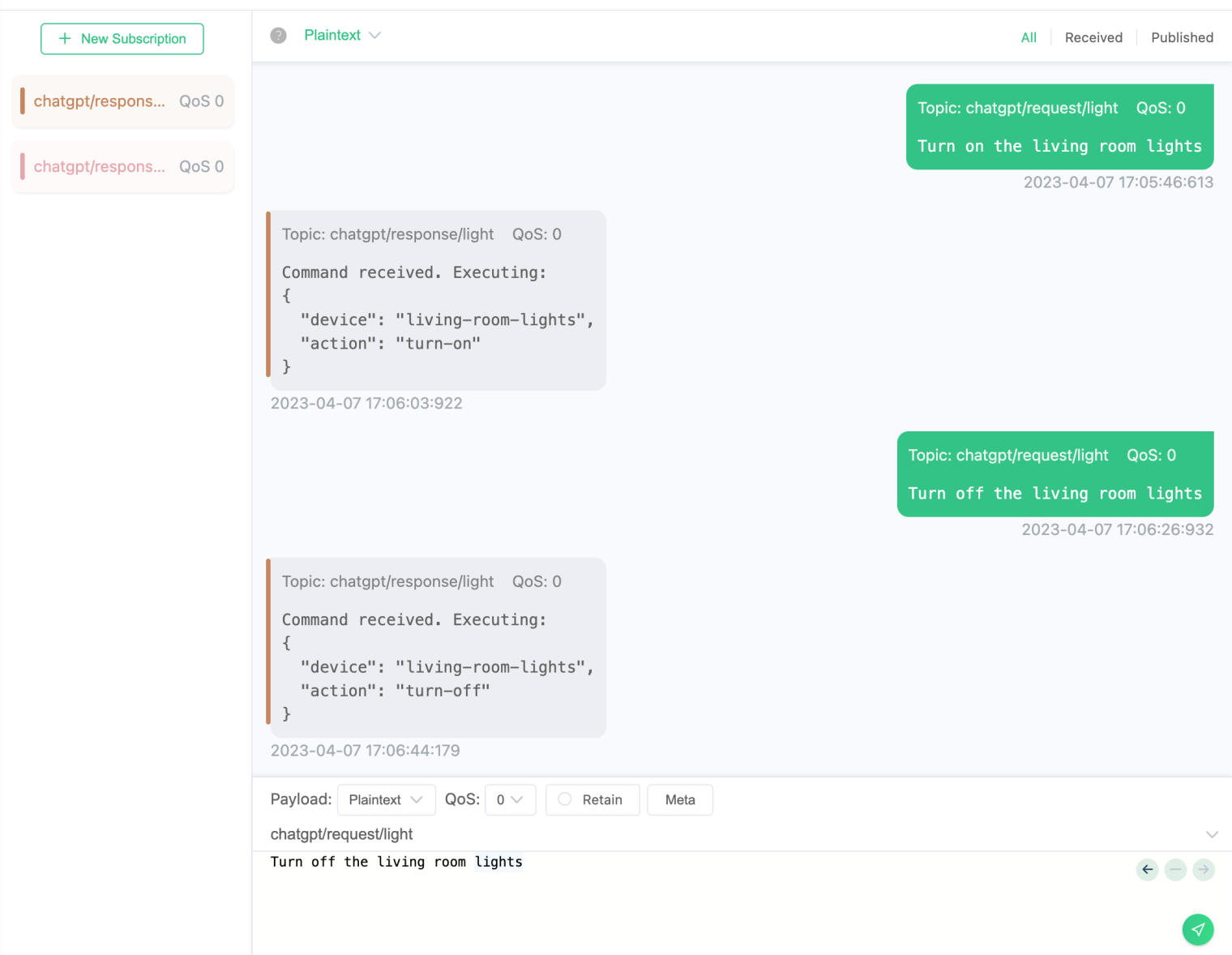
We can also make a smart home environment that includes multiple MQTT topics that match different types of devices (such as lights, air conditioners, sounds, etc.). We will use ChatGPT to generate natural language commands for interacting with these devices in real-time through MQTT clients.
Future Prospects
By combining ChatGPT and MQTT protocol, you can create an intelligent IoT system with vast potential for smart homes and industrial automation. For example, you can use natural language to control your home devices, such as switches, brightness, color, and other parameters, and enjoy a more comfortable living environment. You can also use ChatGPT and MQTT to manage your industrial devices smartly and improve your manufacturing process.
In the future, we can imagine ChatGPT or smarter AGI tools having more of a role in enhancing efficiency and productivity in the IoT field, such as:
Message parsing: Analyze the MQTT messages, extract the relevant data, and prepare for further processing and analysis.
Semantic understanding: Understand and process the meaning of the MQTT messages and extract more accurate information.
Intelligent processing: Use AI technology to process the MQTT messages intelligently and help users find suitable solutions quickly.
User feedback: Receive user feedback through MQTT and respond appropriately as an intelligent interaction agent.
Virtual assistant: Control smart home devices through language recognition technology as a virtual assistant, providing users with smarter and more efficient services and improving the convenience and comfort of life.
Conclusion
This blog delves deep into the integration of MQTT and ChatGPT, revealing the exciting possibilities they offer in various applications. By utilizing EMQX, MQTTX, and the OpenAI API, we explore implementing an AI application similar to ChatGPT. Through seamless data reception and forwarding via MQTT, we successfully demonstrate the integration of MQTT and ChatGPT.
As AI technology becomes more integrated into products (such as New Bing using GPT models for search engines and GitHub's Copilot), we think that the future trends of AI and IoT technologies will also involve enhancing natural language interactions, making device control smarter, and creating more novel use cases. These technologies are not yet part of the production environment but are on the horizon.
In summary, integrating MQTT and ChatGPT shows a promising and exciting field that deserves more attention and research. We hope that these constantly developing innovative technologies will make the world a better place.
